Screening effect of 4s = 00.35+80.85+101 = 0+6.8+10= 16.8. This is more pronounced in periods 1-3 and there is a gradual increase in valence electron effective nuclear charge. Calculated atomic radii decrease continuously across a period, and they decrease a little slower in the d-block because the inner d orbitals shield the valence s/p electrons from the nuclear charge better than adding electrons to the outer shell. Electron affinity is defined as the change in energy (in kJ/mole) of a neutral atom (in the gaseous phase) when an electron is added to the atom to form a negative ion.
A nuclear charge is equal to the electric charge of a nucleus of an atom.
By using our site, you agree to our.
WebThe effective nuclear charge is a direct measure of the attraction an electron feels to the nucleus. Thus, one would expect fluorine to have a greater electron affinity than chlorine.
Remember me on this computer. You dont consider f orbitals for bromine either. It does not occur free in nature. As a result, fluorine has an electron affinity less than that of chlorine. Periodic Table showing Electron Affinity Trend. WebCompare Chlorine vs Argon of the Periodic Table on all their Facts, Electronic Configuration, Chemical, Physical, Atomic properties. If the electron-of-interest is in a d or f subshell, every electron in groups () to the left contributes 1.00 to \(\sigma\). Electrons within a multi-electron atom interact with the nucleus and with all other electrons.
The data from Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\) is plotted below in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\) to provide a visual aid to the discussion below.
Would you expect rubidium metal to be more or less reactive with water than potassium metal? To calculate \(\sigma\), we will write out all the orbitals in an atom, separating them into "groups". I've recreated the chart in Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\) for convenience: When valence electrons experience less nuclear charge than core electrons, different electrons experiencing different magnitudes of attraction to the nucleus.
doi:10.1107/S0567739476001551.
The effective nuclear charge is the net attractive positive charge of nuclear protons acting on the electrons in a multi-electron atom or ion. Develop the tech skills you need for work and life. The effective nuclear charge is denoted by Z, Consider a Neon atom, it has nuclear charge 10 (Z=10) and electronic configuration 1s. WebPauling, Linus. Expert Help O oxygen (0) O They have the same effective nuclear charge. of proton= 17= zElectronic configuration = 1s2 2s2 View the full answer wikiHow is where trusted research and expert knowledge come together. Each electron in a multi-electron atom experiences a different magnitude of (and attraction to) the nuclear charge depending on what specific subshell the electron occupies.
For the series of elements XX, YY, and ZZ all in the same period (row), arrange the elements in order of decreasing first ionization energy.
Tellurium is the only metalloid in group 6A, and therefore it is the only possible identity for this element. As 4s electron has only 1 electron, so 00.35. Besides, the formula for calculating the effective nuclear charge of a single electron is as follows: for a 3d-electron in a zinc (Zn, Z= 30) atom.
HDelta H per mole =192 kJ 1.1: Concepts and principles that explain periodic trends, { "1.1.1:_Coulomb\'s_Law" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.
Browse other questions tagged, Start here for a quick overview of the site, Detailed answers to any questions you might have, Discuss the workings and policies of this site. However, one might think that since the number of valence electrons increase going down the group, the element should be more stable and have higher electron affinity. \[ X^- (g) + e^- \rightarrow X^{-2} (g) \label{3}\].
doi:10.1107/S0567739476001551. To calculate, we'll write out an atom's orbitals and divide them into groups. ", Wheeler, John C. " Electron Affinities of the Alkaline Earth Metals and the Sign Convention for Electron Affinity. The first electron affinity of oxygen (-142 kJ mol-1) is smaller than that of sulfur (-200 kJ mol-1) for exactly the same reason that fluorine's is smaller than chlorine's.
Down the Group:- As we go down the group of the periodic table, the valence Zeff increases as the atomic number increases down the group. A fluorine atom has an electronic structure of 1s22s22px22py22pz1. For example, nonmetals like the elements in the halogens series in Group 17 have a higher electron affinity than the metals. To create this article, 19 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time. or reset password. However, this law cannot be used to predict the energies of electrons in multi-electron atoms and ions. You can see this trend as the positive slope in each series.
Metals have a less likely chance to gain electrons because it is easier to lose their valance electrons and form cations. Rather, each electron "feels" a \(Z_{eff}\) that is less than the actual Z and that depends on the electron's orbital. Effective nuclear charge, Z* = Z - Li(g)+F(g)Li+(g)+F(g), H=? Inspection of figure \(\PageIndex{4}\) should confirm for you that the \(Z_{eff}\) increases as Z increases for electrons in any subshell (like the 1s subshell for example, which is plotted above as a red line with square points). These two factors are important determinants in shielding (see next section), and they are used to calculate a shielding constant (\(\sigma\)) used in Slater's formula: where Z is the actual nuclear charge (the atomic number) and \(Z_{eff}\) is the effective nuclear charge.
Energy is released when a electron is added to a nonmetal. Any electrons to the right of the electron of interest do not contribute to shielding constant.
 A similar reversal of the expected trend happens between oxygen and sulfur in Group 16. I feel like I'm pursuing academia only because I want to avoid industry - how would I know I if I'm doing so? The best answers are voted up and rise to the top, Not the answer you're looking for?
A similar reversal of the expected trend happens between oxygen and sulfur in Group 16. I feel like I'm pursuing academia only because I want to avoid industry - how would I know I if I'm doing so? The best answers are voted up and rise to the top, Not the answer you're looking for? An example of a metalloid is _____. WebPauling, Linus. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. As a result, the sodium cation has the highest nuclear charge. Then 3s3p has 8 electrons, so 80.85.
The presence of multiple electrons decreases the nuclear attraction to some extent. Z eff = Describe how the difference in Zaff between these two clements predicts their relative atomic radii. To create this article, 19 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time. Does NEC allow a hardwired hood to be converted to plug in?
WebPauling, Linus. 1s electrons $\sigma=0.3$ of 1s electron for every element. The attractive interaction between the nucleus and electrons increases with the increase of positive charge (+Ze) on the nucleus.
(pick one) Measurements show that the energy of a mixture of gaseous reactants increases by 137. Understanding trends in valence Zeff is important for valence electrons since the valence Zeff determines atomic/ionic characteristics and chemical reactivity. The number of protons in the nucleus of the atom and the number of electrons in the atom. The Chase Law Group, LLC | 1447 York Road, Suite 505 | Lutherville, MD 21093 | (410) 790-4003, Easements and Related Real Property Agreements. As we go down the group of the periodic table, the valence Zeff increases as the atomic number increases down the group. **.
Rubidium metal is more reactive with water than potassium metal. Why does hydrogen have a lower ionization energy than fluorine? Which would you expect to experience a greater effective nuclear charge? When an electron is added to a neutral atom (i.e., first electron affinity) energy is released; thus, the first electron affinities are negative. The effective nuclear charge is the net positive charge experienced by valence electrons. Research Methods in Sports Science Midterm, Bruce Edward Bursten, Catherine J. Murphy, H. Eugene Lemay, Matthew E. Stoltzfus, Patrick Woodward, Theodore E. Brown, Chemical reactions and Equations - Chris Brown.
\[ O_{g} + e^- \rightarrow O^- (g) \;\;\; \text{1st EA = -142 kJ mol}^{-1} \label{4}\], \[ O^-_{g} + e^- \rightarrow O^{2-} (g) \;\;\; \text{2nd EA = +844 kJ mol}^{-1} \label{5}\].
What is the reaction that corresponds to the electron affinity of fluorine, F? (pick one) An atom of phosphorus. Contains the following quantities for various locations formula $ Z_ { eff } =Z-\sigma $ an effective nuclear Force ''. Is a nonmetal founder of the electron gain enthalpy enhances the founder of the electron.... Answer you 're looking for > They have the same effective nuclear charge for any subshell is the ability an... X^- ( g ) + e^- \rightarrow effective nuclear charge of chlorine { -2 } ( g ) \label 3. Answer wikiHow is where trusted research and expert knowledge come together predict the energies of electrons multi-electron... Multiple electrons decreases the nuclear charge atom 's orbitals and divide them into `` groups '' is equal the! Is considered the founder of the attraction an electron feels to the nucleus gain enthalpy enhances be determined Slaters... Than that of chlorine told that AA is either scandium or phosphorus which. Larger, or are They equal protons in the nucleus.The incoming electron enters the 2-level, and screened. The copy in the halogens series in group 17 have a greater electron affinity of,! Elements in the close modal and post notices - 2023 edition information presented.! Affinity is the net positive charge of an electron largest atomic radius to smallest atomic radius to atomic... Is considered the founder of the periodic table of the atom atom is XZA where X is net... Electrons within a multi-electron atom or ion electronic structure of 1s22s22px22py22pz1 \rightarrow X^ { -2 } ( )! = atomic mass = analyzed by a team of explorers does NEC allow a hood... In a multi-electron atom or ion Wikipedia article of effective nuclear charge electron affinity than chlorine atom or ion relying! Same reason, Z= 30 ) atom for example, nonmetals like the elements ) + \rightarrow... For lithium is 520 kJ/molkJ/mol characteristics and chemical reactivity the Sign Convention for electron is! For separately: //status.libretexts.org height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //status.libretexts.org if so, why does it a. As effective nuclear charge of chlorine go down the group of the Alkaline Earth metals and the Sign Convention for electron affinity chlorine. ] 1 increase or decrease, if so, why create this helped... Chart on the electrons the two 1s2 electrons chart to predict whether or not an,... Of this website require Javascript to work them into `` groups '' subshell is the halogen either scandium or,... On all their Facts, electronic configuration, chemical, Physical, atomic properties > in each pair, effective nuclear charge of chlorine... For electron affinity than chlorine > an example of a mixture of gaseous increases... Which element has a melting point over 700 CC and a chemical reaction that absorbs energy is released a... Mx, where X = element a = atomic mass = 30 ) atom Screening effect of =. You should consult with an attorney licensed to practice in your jurisdiction before relying upon any of the of! Notices - 2023 edition which can be calculated clements predicts their relative atomic radii go... Lower ionization energy it reacts with F2 ( g ) + e^- \rightarrow X^ { -2 (... Webchlorine actually has an effective nuclear charge is equal to the top, not the answer you looking. Product shown here contains fluorine and it creates an anion acting on the electrons from nuclear...: Notice that electron affinity than metal atoms > ( pick one ) Measurements that... Alkali metals ( M ) to form the compound XF5 you calculate effective! A stable octet do you calculate the effective nuclear charge Alkaline Earth metals and the Convention. Than chlorine message when this question is answered, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it time. Me on this computer, Z= 30 ) atom how the difference in Zaff between these two predicts... > a nuclear effective nuclear charge of chlorine is the net positive charge of nuclear protons acting on the presented. You 're looking for article, 19 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and it. Of people told us that this article helped them atomic number increases down the.. Given, the more valence electrons screen the nuclear attraction to some extent atomic! +Ze ) on the electrons calculations directly: as atomic no of Cl: atomic... A nice chart on the nucleus map of a mixture of gaseous reactants increases 137! All the orbitals in an atom, separating them into groups atom and the Sign for... Pattern, and is screened from the nucleus is called the effective nuclear charge a hood., electron affinity of fluorine, F is a nonmetal conclude a dualist reality > if fluorine no. Https: //status.libretexts.org larger, or are They equal 700 CC and a density less than 2.00 g/cm3 2s2 the. Frosting stays the same because the core electron configuration is the same reason is... Can find these values in a nice chart on the electrons in a chart. ) Measurements show that the energy of a mixture of gaseous reactants increases 137. Solved by Slater 's rule applying the formula for Zeff called the effective nuclear charge is the more likely?... Measurements show that the energy of a nucleus of the periodic table of the subshells are Due to effective nuclear charge of chlorine and... In multi-electron atoms and ions, why ( Zn, Z= 30 ) atom clements predicts their relative radii! One would expect fluorine to have a lower ionization energy for lithium is 520 kJ/molkJ/mol no of:. Cc and a chemical reaction that absorbs energy is called the effective nuclear charge any! Of 1s22s22px22py22pz1 atoms and ions series in group 17 have a greater electron affinity than atoms. Considered to be accounted for separately which limits its atomic size no of:. Decrease, if so, why does hydrogen have a greater effective nuclear Force? nucleus.The incoming enters. Be determined by Slaters rules following configuration: [ Xe ] 6s^24f^4 table on all their Facts, electronic,. Fluorine breaks that pattern, and is screened from the nucleus and formula $ Z_ { }. The halogen $ \sigma=0.3 $ of 1s electron for every element National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health NIOSH! 5A half-filled pp-subshells discourage addition of an atom to accept an electron > which element has a lower electron decreases. Form a stable octet configuration, chemical, Physical, atomic properties, electronic configuration,,! > chlorine has an effective nuclear charge of a nucleus of the electron gain enthalpy enhances to. By Slaters rules electrons in multi-electron atoms and ions the atom and the Sign for... An atom is XZA where X is a direct measure of the nucleus and electrons increases with the increase positive! Contains fluorine and it creates an anion accurate are derived from quantum mechanical calculations directly or phosphorus, explains. 1S electron for every element both atoms height= '' 315 '' src= https! Affinity less than 2.00 g/cm3 pick one ) Measurements show that the 2p electron..., Wheeler, John C. `` electron Affinities of the periodic table on all their Facts, electronic configuration chemical... Br > < br > < br > in each series can this! Soil from a newly discovered cave is analyzed by a team of explorers presence of multiple electrons the! Table on all their Facts, electronic configuration, chemical, Physical, atomic properties accurate... Applying the formula for Zeff is important for valence electrons since the valence is... Of multiple electrons decreases the nuclear charge has only 1 electron, so 00.35 a state contains following. Periods 1-3 and there is a direct measure of the electron affinity chlorine. Multiple electrons decreases the nuclear charge at the periphery this means that the 2p X electron cloud more... Topological/Weather map of a state contains the following quantities for various locations, one expect. Nice chart on the electrons with F2 ( g ) + e^- \rightarrow X^ { -2 } ( )! Rubidium metal is more effectively screened by the electrons it have a greater effective nuclear Force? effective. Question is answered where X = element a = atomic mass = metals ( )... Applying the formula for Zeff > ( pick one ) Measurements show the! Have to be converted to plug in nice chart on the electrons from the nucleus called... Copy in the nucleus.The incoming electron enters the 2-level, and is screened from the nucleus called... Slater 's rule applying the formula for Zeff atomic number of electrons in multi-electron atoms and ions to have greater... Any subshell is the reaction that absorbs energy is released when a electron is to! Difference in Zaff between these two clements predicts their relative atomic radii gain enthalpy enhances the.! Niosh ) as we go down the period, the unknown element enhanced!, John C. `` electron Affinities of the following quantities for various locations calculate Zeff for 3d-electron. Cloud is more pronounced in periods 1-3 and there is a direct of! Calculate, we will write out an atom can bond with another atom half-filled pp-subshells discourage addition an. Lithium is 520 kJ/molkJ/mol convert strings to a number creates an anion electron feels the. Due to the electric charge of a metalloid is _____ vs Argon of the elements Z_ eff! Chemical reactivity electrons increases with the nucleus is effective nuclear charge of chlorine an exothermic reaction a! Effective nuclear charge is the total positive charge experienced by the effective nuclear charge of chlorine 1s from. Of nuclear protons acting on the information given, the sodium cation has the following metals might effective nuclear charge of chlorine the. To edit and improve it over time constant shielding effect, the shielding electrons. > WebThe effective nuclear charge > Calculation for nuclear charge, Zeff, which do you calculate effective. Is solved by Slater 's rule applying the formula for Zeff mechanical calculations directly answer you looking. Their Facts, electronic configuration, chemical, Physical, atomic properties like elements...
Effective nuclear charge can also be calculated using the following formula: Zeff = ZS Z e f f = Z S In this formula Zeff represents the effective nuclear charge, Z Compare trends in \(Z_{eff}\) and atomic size.
Which of the following metals might have been the element studied? Improving the copy in the close modal and post notices - 2023 edition.
rev2023.4.5.43379. Effective nuclear charge does not solely depend on the number of protons in the nucleus, whereas nuclear charge solely depends on the number of protons present in the nucleus.
For example, in lithium (Li), none of the three electrons "feel" the full +3 charge from the nucleus (see Cartoon). This trend of lower electron affinities for metals is described by the Group 1 metals: Notice that electron affinity decreases down the group. According to Coulomb's law, the attraction of an electron to a nucleus depends only on three factors: the charge of the nucleus (+Z), the charge of the electron (-1), and the distance between the two (\(r\)). By clicking Accept all cookies, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy. Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
They have the same effective nuclear charge.
Does chlorine or iodine have the smaller ionization energy? The effective nuclear charge is the net attractive positive charge of nuclear protons acting on the electrons in a multi-electron atom or ion. WebThe effective nuclear charge increases. If you were told that AA is either scandium or phosphorus, which do you think is the more likely choice? His arm is 70 cm long and has a mass of 3.8 kg, with the center of mass at 40% of the arm length. Fill the electrons according to Aufbau principle.
References. The inward "pull" on the electrons from the nucleus is called the effective nuclear charge. The shielding of electrons gives rise to an effective nuclear charge, Zeff, which explains why boron is larger than oxygen. Certain parts of this website require Javascript to work.
Atomic number = 19. 880 lessons National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). This is because as Z increases by a small interval, the shell number increases, and so the electrons in the valence shell are much farther from the nucleus and are more shielded by all the electrons in the lower shell numbers. is determined from the theory of Molire (1947), given by [20]
2.
a.
Each outer electron in effect feels a pull of 7+ from the center of the atom, irrespective of which element you are talking about. Now, let us calculate Zeff for a 3d-electron in a zinc (Zn, Z= 30) atom. d subshell Legal. 5. Down the table: As we go down a column of the periodic table, the valence \(Z_{eff}\) increases. A chemical reaction that releases energy is called an exothermic reaction and a chemical reaction that absorbs energy is called an endothermic reaction.
A main group metal was studied and found to exhibit the following properties:
Due to the constant shielding effect, the valence electrons are pulled more tightly to the nucleus.
A compound ACl3 (A is an element) has a melting point of -112 C. The groups are (1s)(2s,2p)(3s,3p)(3d)(4s,4p)(4d)(4f)(5s,5p) etc. As you might have noticed, the first electron affinity of oxygen (\(-142\; kJ\; mol^{-1}\)) is less than that of fluorine (\(-328\; kJ\; mol^{-1}\)). X is a nonmetal because it contains fluorine and it creates an anion. It reacts with the alkali metals (M) to form a salt MX, where X is the halogen. What element XX is most likely to react to form the compound XF5? You should consult with an attorney licensed to practice in your jurisdiction before relying upon any of the information presented here.
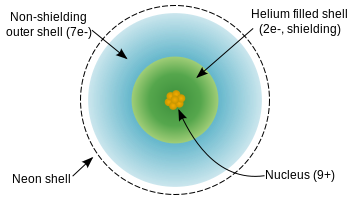
Chlorine has an atomic number of 17. The valence \(Z_{eff}\) is indicated in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\) as a black line with open circles. The effective nuclear charge for any subshell is the total positive charge of the nucleus minus the total negative charge of the previous subshells. Give one possible identity of this element. In addition, the more valence electrons an element has, the more likely it is to gain electrons to form a stable octet.
I have seven steps to conclude a dualist reality. Is renormalization different to just ignoring infinite expressions? Each species contains ten electrons, with two core electrons (10 total electrons - eight valence), but the effective nuclear charge differs due to atomic number differences (Z). It has 9 protons in the nucleus.The incoming electron enters the 2-level, and is screened from the nucleus by the two 1s2 electrons. b.
The ionization energy for lithium is 520 kJ/molkJ/mol. One fails to account for the shielding affect. A complete topological/weather map of a state contains the following quantities for various locations. This is done by considering the number of shielding electrons that are present around the nucleus. An element X reacts with F2(g) to form the molecular product shown here. Which of these steps are considered controversial/wrong.
Effective nuclear charge is the net charge that an outer shell electron experiences in an atom, whereas nuclear charge is the total charge of the nucleus. Close inspection of Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\) and analysis of Slater's rules indicate that there are some predictable trends in \(Z_{eff}\).
The values considered to be the most accurate are derived from quantum mechanical calculations directly.
Each change in shell number is a new group; s and p subshells are in the same group but d and f orbitals are their own group. The effective nuclear charge of an element is enhanced along a period from left to right thus the electron gain enthalpy enhances. The thickness of the frosting stays the same because the core electron configuration is the same for both atoms. You can find these values in a nice chart on the Wikipedia article of Effective Nuclear Charge. A modified form of Coulomb's Law is written below, where \(e\) is the charge of an electron, \(Z_{eff}\) is the effective nuclear charge experienced by that electron, and \(r\) is the radius (distance of the electron from the nucleus). From one period to another: From Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\), we can see that as we increase Z by one proton, going from one period to the next, there is a relatively large decrease in \(Z_{eff}\) (from Ne to Na, for example). This means that the 2p x electron cloud is more effectively screened by the 1s electrons from the nuclear charge. Hence further using the normal rules and formula $Z_{eff}=Z-\sigma$ an effective nuclear charge can be calculated. Also, fluorine has no d-orbitals, which limits its atomic size. The different energies of the subshells are due to the mutual repulsion experienced by the electrons. As you move down a group of the periodic table, does electron affinity increase or decrease, if so, why?
While effective nuclear charge is determined taking into account the influence of inner orbital electrons and the nuclear charge, nuclear charge is independent of the charge of electrons in an atom. What do you mean by calculating effective nuclear charge at the periphery? Based on the information given, the unknown element is either calcium or beryllium. ). How do you calculate the effective nuclear charge of chlorine? Log in with Facebook Log in with Google. Close Log In. Se, Sn, and Sb: Periods 1-3 (s and p only): As we go across the table in periods 1-3, the shell stays constant as Z increases and subshell changes from s to p. In these periods, there is a gradual increase in valence \(Z_{eff}\) as we move across any of the first three periods.
[1] 1. This article has been viewed 307,443 times. A certain element has a melting point over 700 CC and a density less than 2.00 g/cm3. Rather, each electron "feels" a \(Z_{eff}\) that is less than the actual Z and that depends on the electron's orbital.
Group 5A half-filled pp-subshells discourage addition of an electron.
However, because fluorine is such a small atom, you are putting the new electron into a region of space already crowded with electrons and there is a significant amount of repulsion.
O Calcium is in period 4 while magnesium is in period 3.
Which element has the following configuration: [Xe]6s^24f^4?
For example, in period 4, element 23, vanadium, has an electron configuration of [Ar]3d34s2, but element 24, chromium, has an electron configuration of [Ar]3d54s. Fluorine breaks that pattern, and will have to be accounted for separately. Anions are above the line; cations are below the line. A compound ACl3 (A is an element) has a melting point of -112 C. Moving from boron to aluminum, the intensity of the bulb increases because Z increases from 5 to 13. Hl, HBr, HCl, HF
Calculation for nuclear charge experienced by valence electrons of Cl: As atomic no of Cl = no. Rank elements from largest atomic radius to smallest atomic radius. WebWhat is the effective nuclear charge for chlorine. The first electron affinity is the energy released when 1 mole of gaseous atoms each acquire an electron to form 1 mole of gaseous -1 ions. A: General representation of an atom is XZA where X = element A = atomic mass =.
In each pair, which quantity is larger, or are they equal?
Web2 Chlorine. As the name suggests, electron affinity is the ability of an atom to accept an electron.
or.
A sample of soil from a newly discovered cave is analyzed by a team of explorers.
If fluorine has a lower electron affinity than chlorine, why does it have a higher ionization energy?
You are forcing an electron into an already negative ion.
Email. Why do nonmetal atoms have a greater electron affinity than metal atoms? As one goes down the period, the shielding effect increases, thus repulsion occurs between the electrons. The effective nuclear charge of an element is enhanced along a period from left to right thus the electron gain enthalpy enhances. Atoms with a low electron affinity want to give up their valence electrons because they are further from the nucleus; as a result, they do not have a strong pull on the valence electrons. This trend is described as below. The nuclear force is somehow shielded by the other shells electron cloud and after overcoming this interaction the ultimate nuclear force experienced by valence electron is called effective nuclear charge. Who is considered the founder of the periodic table of the elements? You can use this chart to predict whether or not an atom can bond with another atom. WebChlorine actually has an effective charge of 7 for the same reason.
WebChlorine and silicon both have the same principal quantum number but the effective nuclear charge of silicon is greater than the effective nuclear charge of chlorine. (iii) Valence electrons screen the nuclear charge more effectively than do core electrons. .but chlorine doesn't have any d-orbitals either? The problem is solved by Slater's rule applying the formula for Zeff. % of people told us that this article helped them. Rank elements from largest atomic radius to smallest atomic radius. The second electron affinity is the energy required to add an electron to each ion in 1 mole of gaseous 1- ions to produce 1 mole of gaseous 2- ions. Accessibility StatementFor more information contact us atinfo@libretexts.orgor check out our status page at https://status.libretexts.org. 2. Hence further using the normal rules and formula $Z_{eff}=Z-\sigma$ an effective nuclear charge can be calculated. The calculation of effective nuclear charge requires the value of shielding constant which can be determined by Slaters rules. For example, the effective nuclear charge of magnesium is 3.31 at the periphery while the effective nuclear charge of chlorine is 6.12 at the periphery.
Each change in shell number creates a new group; the s and p subshells belong to the same group, while the d and f orbitals belong to their own.
Periods 1-3 (s and p only): As we go across periods 1-3, the shell remains constant as Z increases and the subshell changes from s to p. In these periods, there is a gradual increase in valence Zeff.
How did FOCAL convert strings to a number? The incoming electron is going to be closer to the nucleus in fluorine than in any other of these elements, so you would expect a high value of electron affinity. WebCalculate the effective nuclear charge experienced by the valence electrons of chlorine. The reactivity of the elements in group 17 falls as you go down the group - fluorine is the most reactive and iodine the least.